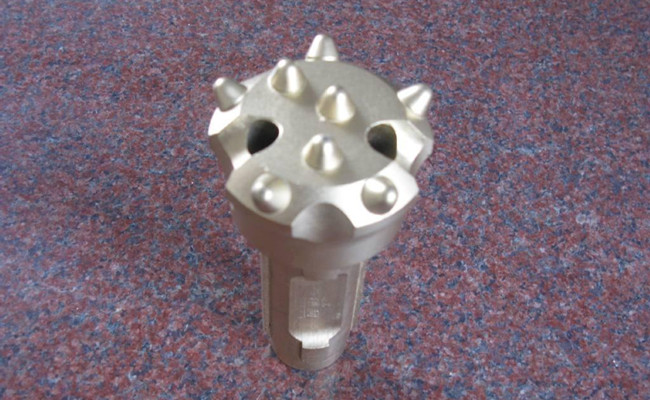
Drilling principle of down-the-hole drill bits
Related products Link:
The name of the down-the-hole drill is named after the DTH hammer (high wind pressure, low wind pressure) penetrates into the bottom of the hole, but other drills do not.
Features of down-the-hole drilling rigs: the principle of rock drilling is the same as that of heavy-duty rock drilling. It is intermittently percussive rock (ore) rock and continuously rotates. The difference is that the impact mechanism of the down-the-hole drilling rig. , The piston directly impacts the drill bit, and continues to advance with the extension of the drill hole. Unlike rock drill rod drilling, the energy loss of a down-the-hole drill increases with the increase of drill rod joints. Because its drill rod does not transmit impact energy, the impact energy loss is small, so deeper holes can be drilled. As the DTH hammer works deep into the hole, the noise on the working surface is greatly reduced. And the drilling accuracy is high.

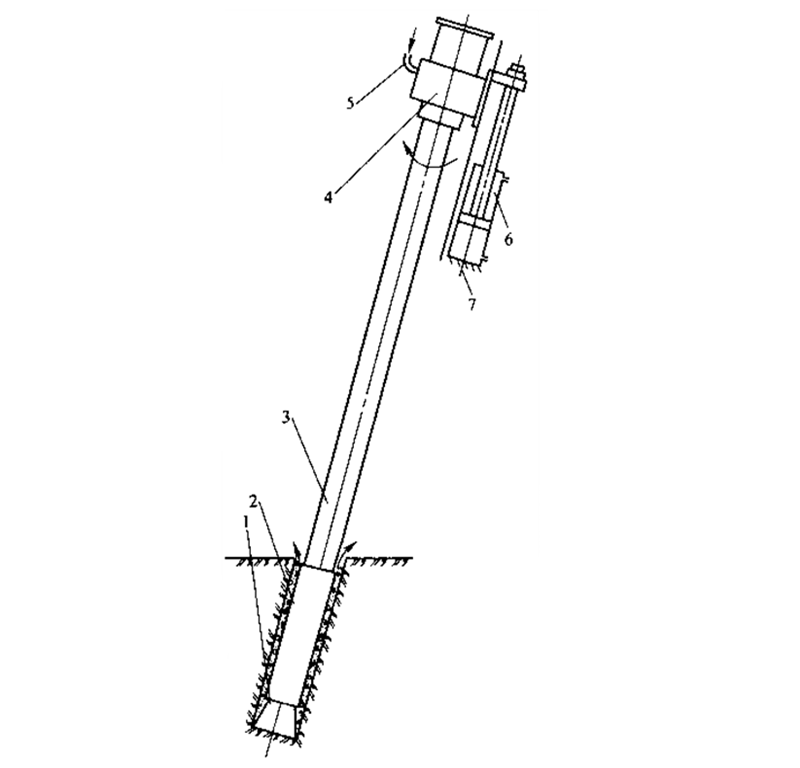
The composition of the down-the-hole drilling rig: It is composed of drill bit 1, impact mechanism (DTH hammer) 2, drill rod 3, slewing mechanism 4, pneumatic joint and operating mechanism 5, pressure regulating mechanism 6, supporting amplitude modulation and lifting mechanism 7. Among them, 1, 2 and 3 are collectively called rock drilling tools, which are composed of drill rods, button bits and DTH hammers. At least two drill rod extensions are required for drilling. The principle of the down-the-hole drilling rig: the pressure regulating mechanism 6 completes the adjustment of the propulsion force to complete the drilling work efficiently. The air compressor is used as the main force and high-pressure air is used as the power to do work. The piston in the compressed air impact mechanism 2 completes the impact drill bit 1 The impact action is realized by the slewing mechanism 4, and the rotation of the drill bit is only used to change the position to avoid repeated crushing. The lifting and amplitude modulation of the drilling rig is completed by the mechanism 7. It is equivalent to adjusting the height of the frame. If the frame is not high, the drill rod cannot be high. Various actions are controlled by the operating mechanism 5. The supporting mechanism can be a bracket or a drill carriage. The cuttings (powder) formed during the drilling process are discharged to the outside of the hole by the gas or water flowing between the drill pipe and the hole wall. Air compressor, power supply and slag blowing. The compressed gas enters the DTH hammer through the drill pipe, and then is discharged from the drill bit. The exhaust gas is used to discharge the ballast. Working principle: During normal drilling, the eccentric drill is driven to drill through the vibration and impact of the DTH hammer. Due to the centrifugal force and friction, the eccentric wheel deflects outwards to achieve the purpose of expanding the hole diameter. Then the casing is driven by the impact of the rod stabilizer to follow up, and the rock powder produced by the drilling is blown out of the hole through the keyway on the rod stabilizer. After the drilling is completed, the eccentric wheel is retracted and the casing is pulled out by reversing, and the casing is left in the hole to protect the wall to form a hole. The casing follow-up is performed by hammering the tube shoe connected to the casing with a down-the-hole hammer to follow up synchronously. Those in charge don't need to reverse and retreat, just lift it up. Unique taper. With variable diameter design, if gravel and soil are stuck during drilling, the taper of the drilling rig can reduce the lifting resistance and greatly reduce the occurrence of failures that the DTH hammer cannot lift. Working principle of eccentric drilling tool: (1) Working principle of eccentric drilling with tube.
Note for drilling rigs: Reasonable shaft thrust DTH rock drilling mainly depends on the impact energy of the drill bit to break the rock (ore). Therefore, DTH rock drilling does not require a large shaft thrust. If the shaft thrust is too large, it will not only easily produce severe vibration, but also accelerate the wear of the cemented carbide, which will damage the bit prematurely; if the shaft thrust is too small, the bit cannot make good contact with the rock (ore), which affects the impact energy transmission Efficiency, even causing the DTH hammer to not work properly.
1 Formula calculation, 2 use reasonable experience if you don’t count, a. Consider that the weight of the drilling component (including drilling tool and rotary air supply mechanism) exerts a force on the bottom of the hole (positive when drilling downwards, negative when drilling upwards) ), it will affect the reasonable shaft thrust. At the same time, there is frictional resistance between the drill rod and the hole wall during drilling. Therefore, the down-the-hole drill must be equipped with a pressure regulating mechanism to adjust the force (thrust) applied to the drill tool. b. Consider the rotation speed of the drill tool. Each time the drill bit impacts, it can only break a certain range of rocks. When the rotation speed of the drill tool is too high, between the two gouge marks, a part of the nodules that have not been broken by impact will inevitably remain, which will increase the rotational resistance torque, increase the vibration of the drill tool, and accelerate the wear of the drill bit, which not only reduces the drilling speed. , And even cause a drill clamping accident; when the rotation speed is too low, repeated crushing may occur, because the impact energy of the drill bit is not fully utilized, the drilling speed is reduced. The optimal number of rotations of the drilling tool should be determined based on the fact that there is no rock tumor or repeated breakage between the two impacts of the drill bit. However, this reasonable angle of rotation is related to many factors such as drill bit diameter, rock properties, impact energy, impact frequency, shaft thrust, bit structure, and the degree of wear of the cemented carbide sheet (column). It is difficult to make accurate calculations, usually only Can be determined based on production experience and experimental methods.




